CO2 Laser Machines: Versatile and Budget-Friendly
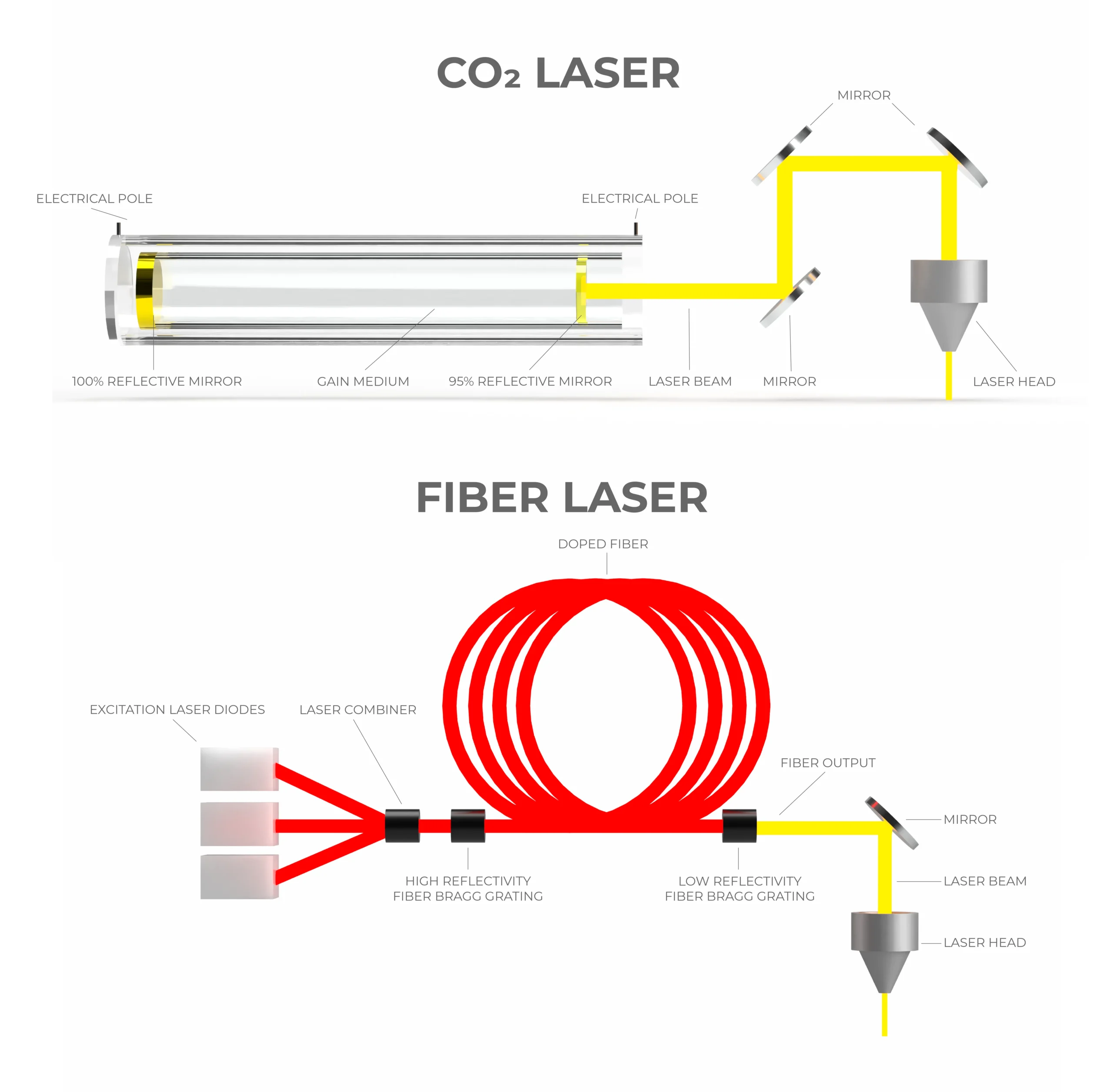
How CO2 Lasers Work
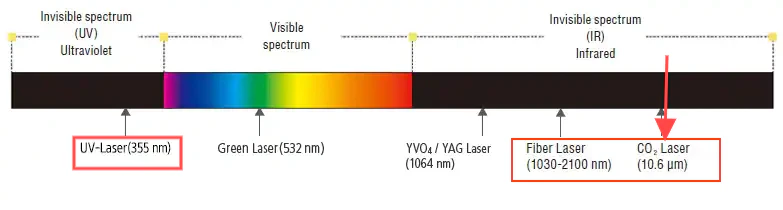
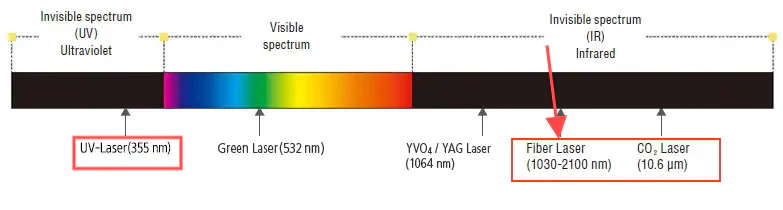
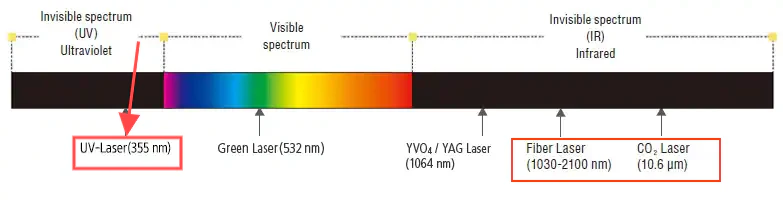
CO2 lasers generate a 10.6-micron wavelength beam using a gas mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium. The beam heats materials to the point of vaporization, enabling cuts and engravings with a precision of 0.1 mm.
Applications
CO2 lasers are ideal for non-metallic materials, including:
- Wood
- Acrylic
- Leather
- Textiles
- Paper
They’re popular in signage, packaging, woodworking, and custom crafting.
Advantages
- Versatility: Processes a wide range of non-metals, perfect for diverse projects.
- Cost-Effective: Entry-level models range from ₹1,71,935 INR to ₹12,89,512 INR, ideal for small businesses.
- Scalable Sizes: Available for small workshops or large industrial setups.
Limitations
- Slower Processing: Less efficient for thick materials compared to Fiber or UV lasers.
- Maintenance Needs: Requires regular tube replacements and lens cleaning, adding to costs.
- Non-Metal Focus: Limited effectiveness on metals without specialized enhancements.


Fiber Laser Machines: Precision for Metals
How Fiber Lasers Work
Fiber lasers use a solid-state source, typically ytterbium-doped fibers, to produce a 1.06-micron wavelength beam. This shorter wavelength excels at cutting and engraving metals and plastics with micron-level precision.
Applications
Fiber lasers dominate in industries like:
- Automotive (e.g., part marking)
- Aerospace (e.g., component engraving)
- Electronics (e.g., circuit board etching)
- Jewelry (e.g., detailed designs)
They also handle certain plastics and coated materials effectively.
Advantages
- High Precision: Achieves details as fine as 1 micron, ideal for intricate work.
- Long Lifespan: Up to 100,000 hours with minimal maintenance.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower power consumption compared to CO2 lasers.
Limitations
- Higher Cost: Prices range from ₹17,19,350 INR to ₹1.03 Cr INR, depending on power output.
- Material Constraints: Less effective for organic materials like wood or textiles.
- Setup Complexity: Requires training for optimal performance.

UV Laser Machines: Ultra-Fine Precision
How UV Lasers Work
UV lasers employ a solid-state ultraviolet source, producing a 355 nm wavelength beam—one-third that of Fiber lasers. Their “cold processing” technique uses photochemical ablation to minimize heat, preserving material integrity and enabling sub-micron precision.
Applications
UV lasers are critical in precision-driven fields:
- Medical device manufacturing (e.g., stents)
- Electronics (e.g., microchip marking)
- Aerospace (e.g., lightweight composites)
- Glass and ceramic engraving
They can also process select organic materials like wood.
Advantages
- Unmatched Precision: Sub-micron details for delicate applications.
- Low Heat Impact: Reduces warping or cracking, ideal for sensitive materials.
- Broad Compatibility: Works on metals, plastics, glass, and some organics.
Limitations
- Premium Cost: Starting at ₹42 Lakh INR, often exceeding ₹85 Lakh INR.
- Limited Power Options: Available in 3W, 5W, or 10W, less suited for heavy cutting.
- Newer Technology: Fewer trained operators and limited market availability.


Direct Comparison of CO2, Fiber, and UV Lasers
| Feature | CO2 Laser | Fiber Laser | UV Laser |
| Wavelength | 10.6 microns | 1.06 microns | 355 nm |
| Best Materials | Non-metals (wood, acrylic) | Metals, plastics | Metals, plastics, glass |
| Precision | 0.1 mm | 1 micron | Sub-micron |
| Cost (Entry-Level) | ₹1,71,935 INR – ₹13 Lakh INR | ₹18 Lakhs – ₹1 Cr INR | ₹42 Lakhs+ |
| Speed | Moderate | Fast | Fast for precision tasks |
| Maintenance | High (tube, lenses) | Low | Low |
| Lifespan | ~10,000 hours | ~100,000 hours | ~50,000 hours |
| Industries | Signage, crafts | Automotive, electronics | Medical, aerospace |
How to Choose the Right Laser
- CO2 Lasers: Perfect for startups, hobbyists, or industries focusing on non-metals like signage or textiles.
- Fiber Lasers: Best for high-volume metal processing in automotive, aerospace, or electronics.
- UV Lasers: Ideal for precision-critical applications in medical or electronics fields where material integrity is paramount.
Conclusion
CO2, Fiber, and UV lasers each bring unique strengths to the table. CO2 lasers offer affordability and versatility for non-metals, Fiber lasers provide durability and precision for metals, and UV lasers deliver unmatched finesse for delicate materials. By understanding your project requirements—budget, materials, and precision—you can select the ideal laser system. Explore industry resources or connect with suppliers for hands-on guidance to elevate your cutting and engraving projects.